fault injection testing
What is fault injection testing?
Fault injection testing is a software testing method that deliberately introduces errors to a system to ensure it can withstand and recover from error conditions. Fault injection testing is typically carried out prior to deployment to uncover any potential faults that might have been introduced during production. Similar to stress testing, fault injection testing is used to identify specific weaknesses in a hardware or software system so that they can be fixed or avoided.
Types of fault injection tests
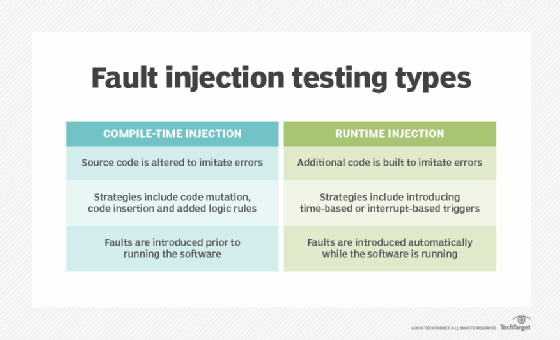
Fault injection testing in software can be performed using either compile-time or runtime injection.
Compile-time injection is a technique in which testers change the source code to simulate faults in the software system. These changes can be implemented by making modifications or mutations to the existing code, such as altering a line of code to represent a different value. Testers can also make changes to code by adding or inserting new code, such as including further logic values.
Runtime injection uses a software trigger to inject a fault into the software while it is running. A trigger can be set to inject a fault at a specified time, known as a time-based trigger. Triggers can also be set using trap mechanisms, which interrupt software at a specific location in the code or event in the system. This is known as an interrupt-based trigger.
Fault injection is comparable to other types of testing such as chaos engineering. However, fault injection differs as it requires a specific approach to test a single condition. Fault injection testing can also be applied to hardware, as it can simulate hardware failures such as shorted connections on circuit boards.
Benefits of fault injection testing
Benefits to fault injection testing include the following:
- Added software resilience.
- Exposure of bugs or errors before they occur naturally in production.
- Opportunity for developers to make changes to previously unknown issues before release.
Fault injection testing tools
Fault injection can be performed manually and does not require additional tools. However, tools can help automate the process.
For example, the testing tool Library-Level Fault Injector, or LFI, automatically identifies errors and injects faults between libraries and applications. Fault Tolerance and Performance Evaluator, or FTAPE, is another automated fault injection tool, which injects faults into memory and disk access. In addition, the Xception tool can help automate the use of software triggers, which trigger faults to memory.



