push notification
What is a push notification?
Push notification, also called server-push notification, is the delivery of information from a software application to a computing device without a specific request from the client.
History/development
Apple first introduced push notifications in 2009, with support for push notifications on iOS devices using the Apple Push Notification service (APNs). The APNs enables app developers to transmit information to iOS, watchOS, tvOS and macOS devices. In 2010, Google launched its own version of the service for Android devices, called Android Cloud to Device Messaging (C2DM), which was replaced by Google Cloud Messaging -- now called Firebase Cloud Messaging -- in 2012.
Google introduced rich notifications and action buttons in 2013, allowing developers to integrate enhanced features into a push notification for Android devices. Android's rich notifications fall into four categories: basic, image, progress and list. Basic notifications include a title, icon and message for more context. Image notifications build upon those features and also include an image preview. Progress notifications also include a progress bar, and list notifications include a list. Action buttons allow users to respond within the notification itself; for example, a user can open the app that requires action or play a song.
Apple followed closely behind in 2014 with the rollout of interactive notifications in iOS 8. Those push notifications allow users to take actions such as replying to text messages and deleting emails directly from the lock screen. In 2015, Apple released the Apple Watch and enabled push notifications for that device.
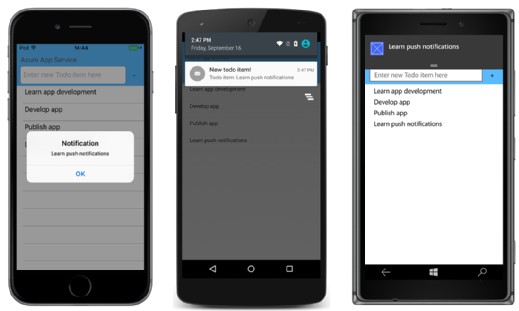
How they work
Unlike pull notifications, in which the client must request information from a server, push notifications originate from a server. Typically, the end user must opt in to receive alerts; opt-in usually takes place during the install process, and end users are provided with a way to manage alerts if they change their minds later on.
Different devices and services rely on different methods to deliver push notifications. Apple developers, for example, can use the APNs Developers application programming interface (API) to have their apps deliver push notifications to iOS devices.
Another approach is to use mobile backend as a service (mobile BaaS) cloud services to provide push notification functionality for a mobile app. Push notification services such as Firebase Cloud Messaging, Amazon Simple Notification Service and Azure Notification Hubs can integrate notifications across mobile devices. Other third-party options, such as Airship and Pushwoosh, can provide more complex data analytics and marketing analysis.
Types of push notifications
There are two main types of notifications for iOS and Android: local notifications and remote notifications. Developers build and configure local notifications within an app. Remote notifications, also called push notifications, enable IT professionals, marketers and developers to send notifications at certain times to specific demographics of their user base.
There are a variety of push notification types that cater to different uses and needs. A standard push notification sends a single notification to a user's device. Geolocation-based notifications, however, enable the app to access the user's location setting, and then developers, marketers and IT can send notifications based on that information. For example, the Yelp mobile app notifies users about new restaurants in their area.
IT, developers, marketers and the like can also schedule recurring push notifications based on a specific business need. For example, a business with a particular weekly special discount might want to send a notification to its user base to advertise the deal.
What they're used for
Push notifications can provide value to both end users and businesses. Users can receive convenient updates in real time, such as weather reports, news updates or flight information. Businesses, on the other hand, can communicate directly to users and encourage them to use the app via specific call-to-action messaging. Push notifications can increase click-through rates, promote products or offers and drive users to other marketing channels.
An important advantage of push notifications in mobile computing is that the technology doesn't require specific applications on a mobile device to be open in order for a message to be received. This allows a smartphone to receive and display social media or text message alerts even when the device's screen is locked and the social media application that is pushing the notification is closed.
The effectiveness of push notifications often depends on the type of app. Ride-sharing mobile apps, such as Uber and Lyft, for example, have high opt-in rates because users often receive valuable and time-sensitive updates. News content and social media apps often have lower opt-in rates, however, because they can overload users with irrelevant information.
See also: contextual marketing messages.



