Malay leid
| Malay | |
|---|---|
| Bahasa Melayu بهاس ملايو | |
| Native tae | Indonesie (as Indonesian) Malaysie (as Malaysian) |
Native speakers | 77 million (2007)[2] Tot: mair nor 215 million[3] |
Staundart forms | |
| Latin (Malay alphabet) Arabic (Jawi)[4] Thai (in Thailand) Historically Pallava, Kawi, Rencong | |
| Offeecial status | |
Offeecial leid in | Cocos (Keeling) Islands (de jure) |
Recognised minority leid in | o a regional leid in Sumatra apart frae the naitional staundart o Indonesian) |
| Regulatit bi | Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka (Institute o Leid an Literatur); Majlis Bahasa Brunei–Indonesia–Malaysia (Brunei–Indonesie–Malaysie Leid Council – MABBIM) (a trilateral jynt-venture) |
| Leid codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ms |
| ISO 639-2 | may (B) msa (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | zlm – inclusive codeIndividual codes: zsm – Malaysianind – Indonesianlrt – Larantuka Malay ?kxd – Brunei ?meo – Kedah Malay ?zmi – Negeri Sembilan Malay ?dup – Duano ?jak – Jakun ?orn – Orang Kanaq ?ors – Orang Seletar ?tmw – Temuan ? |
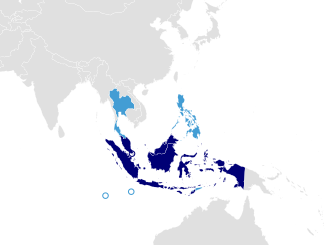 | |
Malay is a major leid o the Austronesian family. Staundartized varieties o Malay are the offeecial leid o Malaysie (Malaysian), Indonesie (Indonesian) an Brunei. Malay is ane o fower offeecial leids o Singapore, an is a wirkin leid o East Timor, a consequence o ower twintie years o Indonesian administration. It is spoken natively bi 40 million fowk[5] athort the Malacca Strait, includin the coasts o the Malay Peninsula o Malaysie an soothren Thailand, Riau province, the eastren coast o Sumatra, an the Riau Islands in Indonesie, as haes been establisht as a native leid o Jakarta an o pairt o wastren coastal Sarawak an Kalimantan in Borneo. As a seicont leid, Indonesian is spoken bi an estimatit 140 million.[6]
In Malaysie, the staundart leid is cried Bahasa Malaysia "Malaysian leid". In Singapore, Brunei, soothren Thailand, an the soothren Philippines it is cried Bahasa Melayu "Malay leid", an in Indonesie it is generally cried Bahasa Indonesia, "Indonesian leid", though Bahasa Nasional "Naitional Leid" and Bahasa Persatuan/Pemersatu "Unifyin Leid" are an aa heard. Housomeivver, in auries o Sumatra an Riau whaur the leid is indigenous, Indonesians refer tae it as Bahasa Melayu.
Oreegin
[eedit | eedit soorce]There are mony hypotheses as tae whaur the Malay leid oreeginatit. Ane o these is that it came frae Sumatra island. The auldest inscriptions in Malay, date frae the end o the 7t century AD, wur foond on Bangka Island, aff the sootheastren coast o Sumatra (the Kedukan Bukit Inscription) an in Palembang in soothren Sumatra. "Malayu" wis the name o an auld kinrick locatit in Jambi province in eastren Sumatra. It wis kent in auncient Chinese texts as "Mo-lo-yo" an mentioned in the Nagarakertagama, an auld Javanese epic written in 1365, as ane o the "tributary states" o the Majapahit kinrick in eastren Java.
The uise o Malay throughoot insular an peninsular Sootheast Asie is linked tae the rise o Muslim kinricks an the spread o Islam, itsel a consequence o growin regional trade. At the time o European colonization, the Johor-Riau Sultanate haed ascendancy. Syne the 15t century, the Johor-Riau dialect o Malay haed been uised as a lingua franca throughoot the Malay Archipelago, as the similar dialect o Malacca haed been uised afore it. When Johor-Riau wis dividit atween Breetish Malaya (Johor) an the Dutch East Indies (Riau), its leid wis accordit offeecial status in baith territories.
Indonesie pronoonced Riau (Johor) Malay its offeecial leid (Bahasa Indonesia) when it gained unthirldom. Syne 1928, naitionalists an young fowk throughoot the Indonesian archipelago haed declared Malay tae be Indonesie's ae offeecial leid, as proclaimed in the Sumpah Pemuda "Youth Vow." Thus Indonesie wis the first kintra tae designate Malay as an offeecial leid.[7]
In Malaysie, the 1957 Article 152 o the Federation adoptit Johor (Malacca) Malay as the offeecial leid (Bahasa Malaysia). The name "Malaysia", in both leid an kintra, emphasized that the naition consistit o mair nor juist ethnic Malays. In 1986 the offeecial name wis chynged tae Bahasa Melayu, but in 2007 it wis chynged back.[8]
"Bahasa Melayu" wis defined as Brunei's offeecial leid in the kintra's 1959 Constitution.
The Indonesian an Malaysian dialects o Malay are separatit bi some centuries o different vocabulary development, pairtly due tae the influence o different colonial leids; Dutch in the case o Indonesie, umwhile the Dutch East Indies, an Inglis in the case o Malaysie, Singapore, an Brunei, which wur umwhile unner Breetish rule. Housomeivver, Indonesie an Malaysie lairgely unified their previously divergent orthographies in 1972, an they alang wi Brunei hae set up a joint commission tae develop common scientific an technical vocabulary an itherwise cooperate tae keep their staundarts convergent.
Some Malay dialects, housomeivver, show ae limited mutual intelligibility wi the staundart leid; for example, Kelantanese or Sarawakian pronunciation is difficult for mony fellae Malaysians tae unnerstaund, while Indonesian contains mony wirds unfamiliar tae speakers o Malaysian, some acause o Javanese, Sundanese or ither local leid influence, an some acause o slang.
The leid spoken bi the Peranakan (Straits Cheenese, a hybrid o Cheenese settlers frae the Ming Dynasty an local Malays) is a unique patois o Malay an the Hokkien Cheenese, which is maistly spoken in the umwhile Straits Settlements o Penang an Malacca in Malaysie, an the Indonesian Archipelago.
References
[eedit | eedit soorce]- ↑ Influences come maistly frae Indonesie
- ↑ Nationalencyklopedin "Världens 100 största språk 2007" The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007
- ↑ Uli, Kozok (10 Mairch 2012). "How many people speak Indonesian". University of Hawaii at Manoa. Retrieved 20 October 2012.
Even if we are very conservative and consider only two third of Malaysians and 85% of Indonesians as fluent speakers (either native, or near-native), there are still more than 215 million speakers of Malay-Indonesian.
- ↑ "Kedah MB defends use of Jawi on signboards". The Star. 26 August 2008. Archived frae the original on 4 September 2008. Retrieved 25 August 2021.
- ↑ 10 million in Malaysie, 5 million in Indonesie as "Malay" plus 23 million as "Indonesian", etc.
- ↑ Ethonologue, "Indonesian"
- ↑ Languages of Indonesia (Sumatra)
- ↑ Penggunaan Istilah Bahasa Malaysia Dan Bukan Bahasa Melayu Muktamad, Kata Zainuddin. BERNAMA, 5 November 2007
| Wikimedia Commons haes media relatit tae Malay language. |