GPS coordinates
What are GPS (global positioning system) coordinates?
GPS coordinates are a unique identifier of a precise geographic location on the earth, usually expressed in alphanumeric characters.
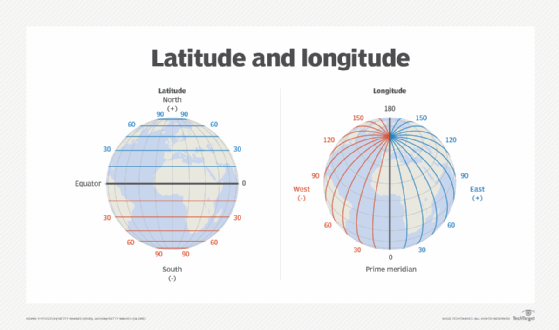
Coordinates, in this context, are points of intersection in a grid system. GPS coordinates are usually expressed as the combination of latitude and longitude. Lines of latitude coordinates measure degrees of distance north and south from the equator, which is 0 degrees. The north pole and south pole are at 90 degrees in either direction. The prime meridian, located in Greenwich, UK, is 0 degrees longitude, and the lines of longitude coordinates are measured according to 90 degrees east and west from that point.
GPS coordinates are expressed in two different formats. Below are the coordinates for the Empire State Building in New York City:
N40° 44.9064', W073° 59.0735'
That same information can be expressed in a purely numeric format:
40.748440, -73.984559 (decimal degrees)
In the numeric format, the minus sign before the second number indicates that the location is west of the prime meridian; a minus sign in front of the first number would indicate degrees south of the equator.
How GPS is deployed
Orbiting above the earth's surface at precise positions is a satellite constellation of 24 GPS satellites. Each one is referred to as a bird and uses radio waves to communicate with other satellites to determine an exact location on the earth. These satellites use the World Geodetic System, known as WGS84, as its reference coordinate system. WGS84's coordinate origin is the center of the Earth.
Position data is transmitted via radio signals to ground-based devices, or transceivers, that receive position information from three or more satellites and convert that data, using specialized software, into visual information. This visual information can be displayed on a video screen, such as those used in automobiles and airplanes.
The software in these air-ground GPS transceivers converts the position data into visual maps or other geographical representations. GPS users can also obtain the actual map coordinates if they wish.
GPS data and applications are accessible on watches and other handheld devices, laptop computers and any information system that can send and receive GPS data.
The U.S. government owns the GPS system, and the U.S. Department of Defense maintains it because its original purpose was for military applications. Nonmilitary users first got access to this data in the 1990s. Today, GPS is a resource available virtually anywhere on the planet.
Devices that use GPS data
Garmin and Magellan are two manufacturers of GPS devices. These devices come in various sizes and support numerous applications. Software built into each device links to GPS satellites and converts GPS data into visual images or audio messages to identify the shortest or most efficient route to a desired location.
GPS location data is often integrated with smart highway technology that gathers information on vehicular traffic activity. Integrated GPS systems provide a primary route to a destination and also generate suitable alternate routes in case of traffic congestion. Systems can also locate places of interest and provide additional options.
Applications of GPS data
GPS data is used in a variety of apps and embedded systems, including the following:
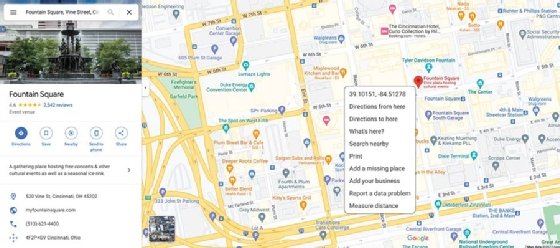
- Mapping software, such as Google maps, uses GPS data when presenting current location data visually.
- GPS data and devices are in motor vehicles, marine vessels, fleet tracking and management systems, smartwatches, smart handheld devices and laptop computers.
- GPS capabilities are often incorporated into digital accessories for outdoor activities such as cross-country running, skiing and hiking.
Geolocation data is part of the structured data included in modern data collection efforts. Find out more about all the elements of big data collection.