Ecologistics
Low carbon freight for sustainable cities


ICLEI’s “EcoLogistics: Low carbon freight for sustainable cities” project focuses on capacitating governmental and non-governmental actors to build strategies and policies to promote low-carbon and more sustainable urban freight through local action and national support.


Project approach
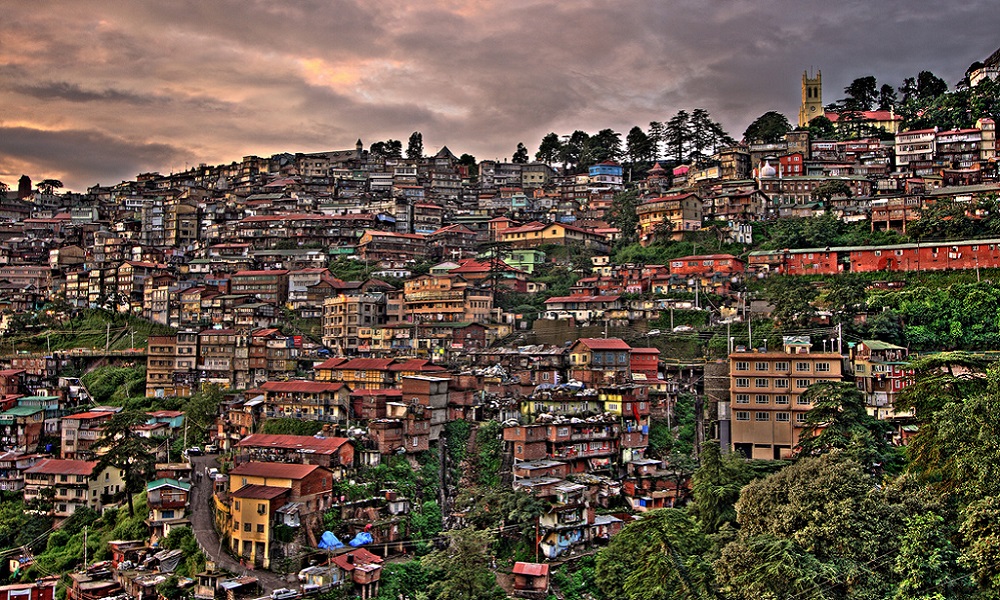
The goal of this project is to promote low carbon urban freight (EcoLogistics) policies and practices contributing to climate change mitigation and towards meeting the ambitions of NDCs in Argentina, Colombia and India.
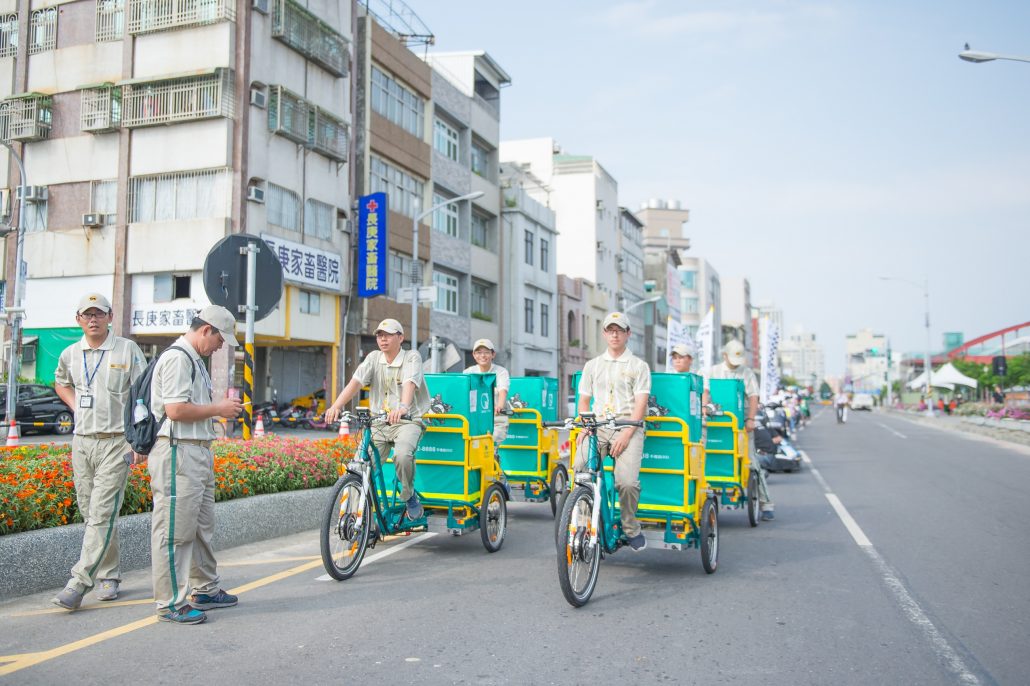
“EcoLogistics” promotes transportation of goods by giving priority to health, safety, people-centered urban development and low-emission and will encourage circular and regional economies to limit the growth of freight transport. It follows the strategy to Avoid (and reduce) the freight volume and haul distance, Shift (and maintain) to more sustainable modes of freight transportation, Improve the logistics operations by use of technologies and better operation.
Project outputs
Project activities
https://carbonn.org/
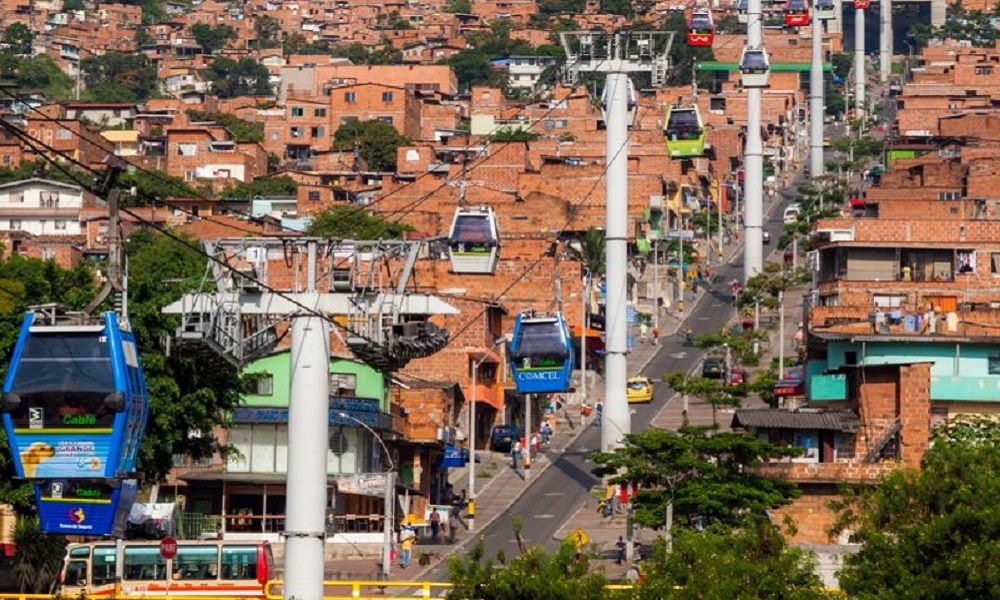
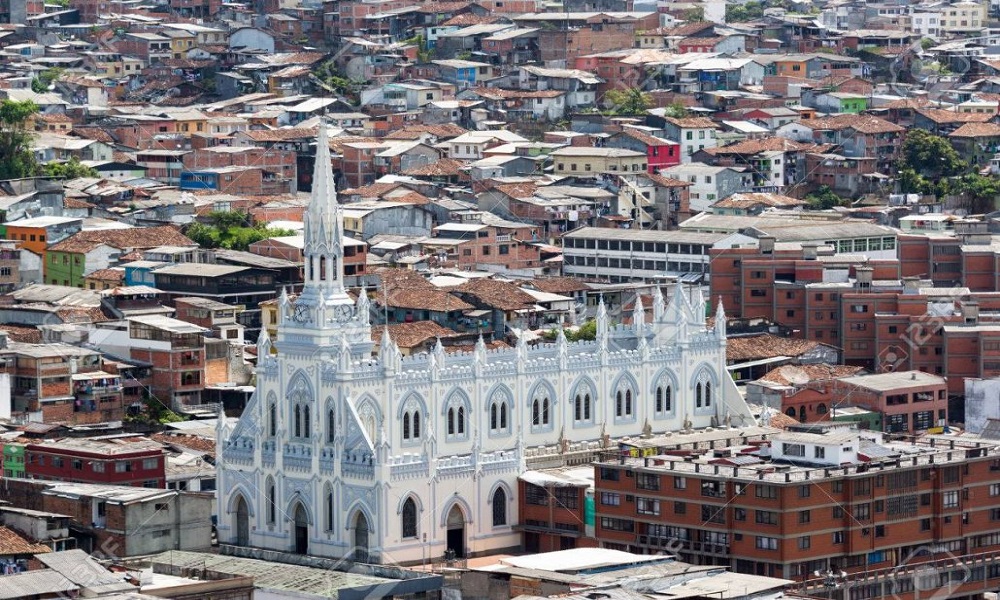
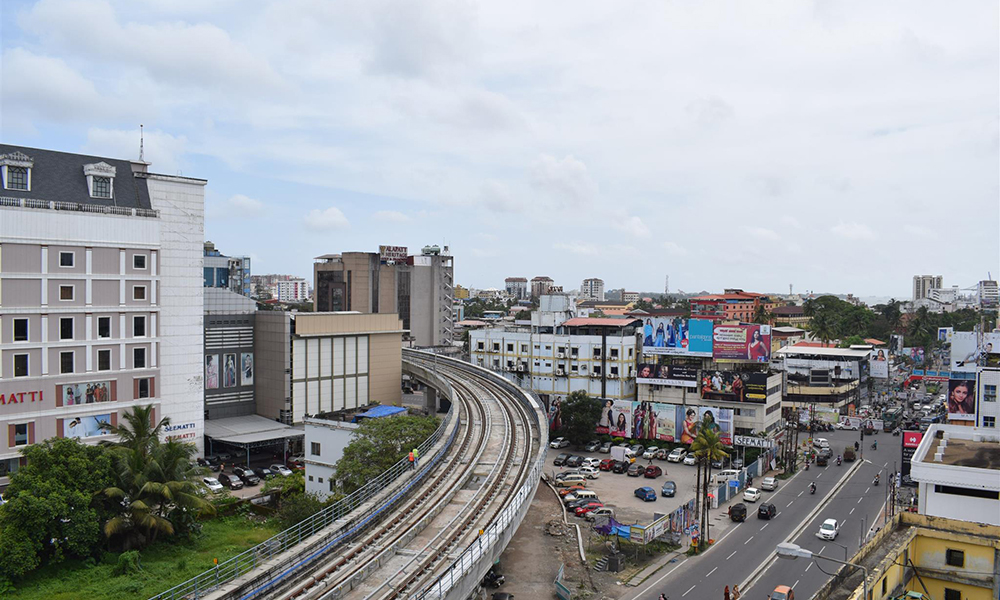
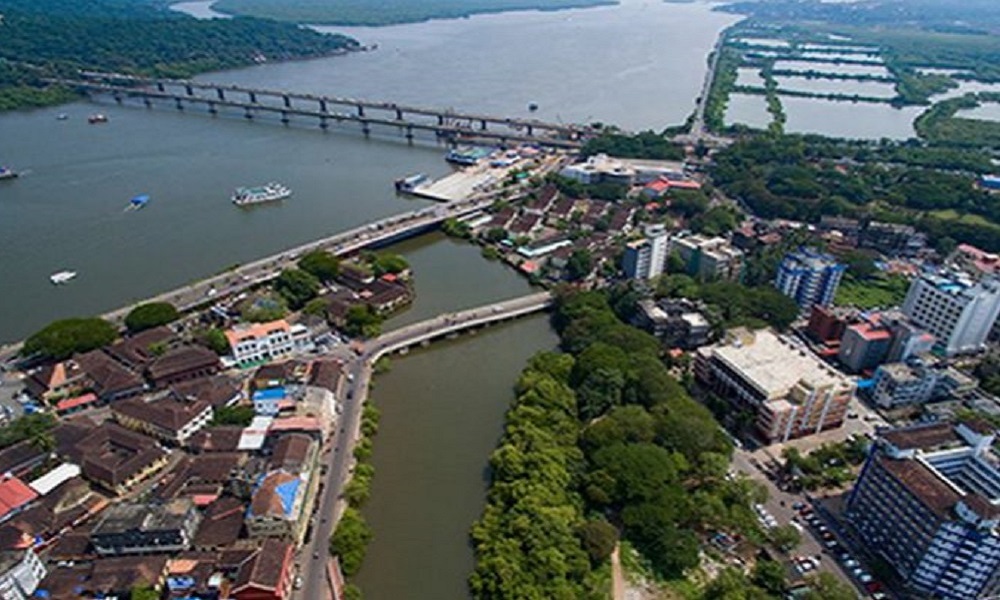
Project cities
Project partners
IKI EcoLogistics is a project implemented by ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability. The ICLEI World Secretariat is responsible for project management and coordination. ICLEI South America Secretariat and ICLEI South Asia Secretariat are the implementing partners. Despacio, the Smart Freight Centre and the Zaragoza Logistics Center are technical partners for this project.
The project is supported by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) through the International Climate Initiative (IKI).
Read more: www.international-climate-initiative.com
Any person who believes they may be harmed by an IKI project or who wish to report corruption or the misuse of funds, can lodge a complaint to the IKI Independent Complaint Mechanism at IKI-complaints@z-u-g.org. The IKI complaint mechanism has a panel of independent experts who will investigate the complaint. In the course of the investigation, we will consult with the complainant so as to avoid unnecessary risks for the complainant. More information can be found at: https://www.international-climate-initiative.com/en/about-iki/values-responsibility/independent-complaint-mechanism/
Project updates